Augmented Reality (AR) has transformed the way we interact with technology, blending the digital and physical worlds in ways that once seemed impossible. Every time I see an AR-powered app, I’m amazed by how it enhances user experiences, making them more immersive and engaging. From gaming to education, AR is reshaping industries and redefining what’s possible in app development.
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) blends digital content with the physical world, creating interactive experiences through real-time environments on devices like smartphones and AR glasses.
What is AR?
AR incorporates computer-generated elements like:
- images
- sounds
- animations
into the user’s real-world environment. These elements appear on screens through AR-enabled apps, merging the virtual and physical worlds. For example, AR applications in retail allow users to see how furniture looks in their homes before purchase.
AR relies on advanced technologies like GPS, cameras, and sensors for accuracy. Marker-based AR uses predefined visual triggers, while markerless AR operates using device location and orientation.
How AR Differs from Virtual Reality (VR)
AR overlays virtual objects on the real world, while Virtual Reality (VR) creates entirely immersive digital environments, replacing the real surroundings. Users remain aware of their physical environment with AR, but VR fully immerses them, often using headsets that block out the outside world.
AR applications enhance real-world scenarios such as training simulations, while VR applications focus on wholly immersive experiences, such as gaming or virtual tours. For instance, AR apps like Pokémon GO integrate virtual elements into real locations, whereas VR creates completely separate spaces.
The Growing Role of AR in App Development
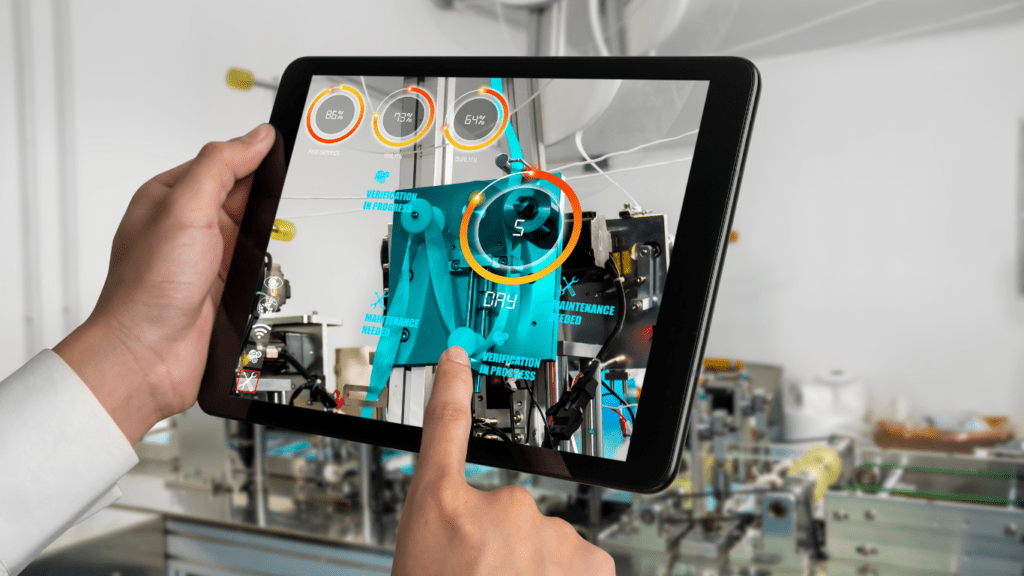
Augmented Reality (AR) continues to redefine app development by merging real-world environments with digital enhancements. Its integration has expanded across diverse sectors, driving creativity and innovation.
Key Industries Leveraging AR Technology
- Healthcare drives AR adoption through surgery simulations and medical training. Applications enable immersive procedures, improving precision and doctor training outcomes.
- Retail transforms shopping by incorporating AR for virtual try-ons and product visualizations. IKEA’s AR app, for instance, lets users see furniture in their homes before purchase.
- Education uses AR to create interactive learning experiences. Apps integrate digital overlays to teach complex subjects, like anatomy, in an engaging, visual manner.
- Gaming remains a prominent AR domain. Games like Pokémon GO exemplify AR’s ability to combine real-world locations with interactive virtual elements, increasing user engagement.
Recent Advances in AR Applications
- AR-capable devices now support spatial awareness and motion tracking. Apple’s ARKit and Google’s ARCore bring such capabilities to developers, enhancing app functionality.
- 5G networks improve AR performance by enabling low-latency and real-time data updates. Developers leverage this for smoother, more immersive AR experiences.
- AI integration enhances AR, introducing features like object recognition and environmental mapping. These advancements make AR applications more intuitive and context-aware.
Benefits of AR in App Development
AR introduces transformative benefits to app development, offering innovative solutions that redefine user interaction, engagement, and problem-solving.
Enhanced User Experiences
AR apps create immersive environments by integrating 3D models, animations, and real-time overlays. Features like virtual product previews in retail apps or AR-based navigation in travel platforms enhance usability and bring interactive elements to everyday tasks. This personalization makes experiences more intuitive and visually stimulating.
Improved Engagement and Retention
Integrating AR into apps boosts user engagement by providing dynamic and context-aware experiences. For instance, AR games like Pokémon GO keep users returning with real-world interaction elements. These features encourage consistent app usage, increasing retention rates and fostering customer loyalty.
Streamlined Problem-Solving Capabilities
AR helps resolve complex challenges by providing visual and interactive solutions. Applications in fields like maintenance and repair use real-time AR overlays to guide users step-by-step. Medical apps utilize AR for precise diagnostics and surgical planning, offering professionals and end-users actionable insights efficiently.
Challenges and Limitations of AR in App Development
Augmented Reality brings innovation, but it also introduces challenges that developers must address for successful app implementation. These limitations primarily relate to technical barriers, cost implications, and accessibility constraints.
Technical Barriers
AR development depends on complex technologies like spatial mapping, real-time rendering, and motion tracking. Ensuring accuracy and seamless performance across diverse environments presents a significant challenge. For example, AR apps often struggle with poor lighting or uneven surfaces, leading to reduced object stability. Compatibility issues with different devices and operating systems further complicate development, requiring extensive testing to ensure consistent functionality.
Cost Implications
AR app development involves high initial investment due to specialized infrastructure and skilled development teams. Costs for building 3D models, acquiring AR SDKs (Software Development Kits), and integrating advanced features like object recognition or location-based AR can quickly escalate. Furthermore, ongoing expenses for updates, bug fixes, and platform compatibility increase operational costs, limiting AR adoption for smaller businesses.
User Accessibility and Hardware Requirements
AR apps rely on hardware with robust processing capabilities, such as AR-enabled smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. Many users lack access to such advanced devices, restricting app usage. For instance, older phone models may fail to support AR features, lowering the potential user base. Additionally, sustained use of AR apps demands significant battery power, which can deter users from engaging with AR-intensive applications for extended periods.

 Frank Gilbert played an instrumental role in shaping the foundation of Code Hackers Elite. With a sharp eye for innovation and deep expertise in software architecture, Frank was central in building the technical framework that powers the platform today. His commitment to clean, scalable code and forward-thinking development practices helped establish a strong backbone for the site, ensuring that the delivery of tech news and coding resources remains seamless and efficient for users worldwide.
Frank Gilbert played an instrumental role in shaping the foundation of Code Hackers Elite. With a sharp eye for innovation and deep expertise in software architecture, Frank was central in building the technical framework that powers the platform today. His commitment to clean, scalable code and forward-thinking development practices helped establish a strong backbone for the site, ensuring that the delivery of tech news and coding resources remains seamless and efficient for users worldwide.
